LED Strips SERIES and PARALLEL circuit connection guide
- By Lumistrips LED Professional
- Jul 2, 2021
Basic LED principles:
An LED (light-emitting diode) is a semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it. Light is energy in the form of photons that emit when electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes.
The higher the current flow, the brighter the LED becomes. However, the circuit is not perfect and some of the current is converted to heat instead of light. When the current reaches a certain value, the heat generated is so high that the semiconductor is permanently damaged. In most LED data sheets, this important limit is specified as "Absolute Maximum Current".
Even if the LED operates below the maximum current, the heat will slowly damage the LED, causing its luminous flux (light output) to gradually decrease. The time when the LED luminous flux is only 70% of the initial value is commonly referred to as "LED life".
For LEDs to have a very long life of 50,000h or more, a current level well below the absolute maximum current is required, which is referred to as the "typical" or "recommended" current.
Constant current source for the recommended current
To operate an LED at the recommended current requires an external circuit, a constant current source. Without it, the current in the LED increases exponentially with the applied voltage, as a small change in voltage results in a large change in current until the maximum current is reached and the LED burns out.
The external circuit, constant current source can be a simple resistor for low power LEDs (max 100mA at 3V) or a stand-alone device called an LED driver.
LED drivers come in many shapes, sizes and power levels and many accept 230 VAC input. Some dedicated LED drivers accept VDC inputs at higher levels than the output (buck converters) or lower levels (boost converters).
A common characteristic of LED drivers is that they provide a constant current output (CC out) within a voltage interval. This output voltage interval is specified in the LED driver data sheet. For example, an LED driver with 350mA CC output at 1-10V can safely power an LED if the voltage required for 350mA is within the 1-10V interval. Examples include a red LED 2V @ 350mA, a white LED 3V @ 350mA, or a COB LED 9V @ 350mA.
Theoretically, it is optimal to use one LED driver for each LED, an approach that is impractical from many points of view, for most LED types. Exceptions are the COB LEDs with very high power, from 50W upwards.
Series and parallel electrical circuits
To light up a string or array of LEDs from one LED driver, the LEDs must be connected into an electrical circuit. This can be a series or a parallel circuit.
We will explain these circuits with examples using our popular LumiBar 56 cm LED strips, such as those with SunLike TRI-R CRI98+ LEDs:
1. Series connection with LumiBar Sunlike CRI98+ LED strips:
One LumiBar 56 cm Toshiba-SSC LED Strip Zhaga Sunlike CRI97 warm white 2700K has the recommended current at 350mA, reached at the voltage of 39.5VDC.
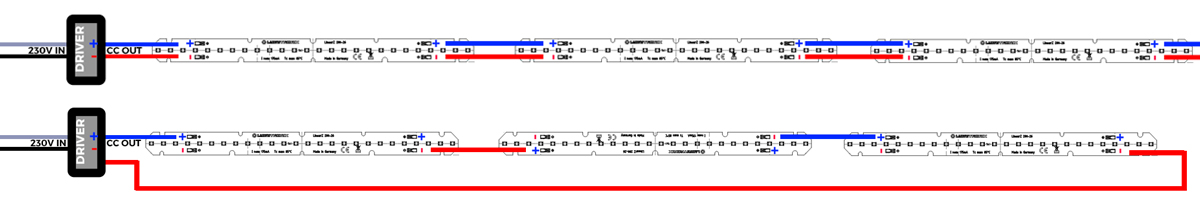
A series circuit with two, three or four LumiBar LED strips is shown below:
The series connection is applied by connecting the positive (+) terminal of the first LED strip to the negative (-) terminal of the second LED strip. This pattern is repeated for further LED strips, from the negative (-) of the second strip to the positive (+) of the third strip and so on. At the same time, the negative (-) of the first LED strip is wired to the (+) of the second, then the (-) of the second to the (+) of the third and so on.
In a series connection of LED strips, the current of the string is equal to the current of the first LED strip, while the voltage is the sum of the voltages for all LED strips (voltage of the first LED multiplied by the number of LED strips):
1 x LumiBar 56 cm Sunlike CRI98+ LED strip: 350mA at 39.5VDC
2 x LumiBar 56 cm Sunlike CRI98+ LED strips in series: 350mA at 79VDC (= 39.5VDC x 2)
3 x LumiBar 56 cm Sunlike CRI98+ LED strips in series: 350mA at 118.5VDC (= 39.5VDC x 3)
4 x LumiBar 56 cm Sunlike CRI98+ LED strips in series: 350mA at 158VDC (= 39.5VDC x 4)
2. Parallel connection
The parallel circuit is applied by connecting the positive (+) of the first LED strip to the (+) of the second LED strip. This pattern is repeated for further LED strips, from the (+) of the second strip to the (+) of the third strip and so on.
At the same time the negative (-) of the first LED strip is wired to (-) of the second, then (-) of the second to (-) of the third and so on.
In a parallel circuit of LED strips, the current of the string is the sum of all current values of the strips, while the voltage is equal with the one of the first LED strip:
1 x LumiBar 56 cm LED strip: 350mA at 37.5VDC
2 x LumiBar 56 cm LED strips in parallel: 700mA(= 350mA x 2) at 37.5VDC
3 x LumiBar 56 cm LED strips in parallel: 1050mA(= 350mA x 3) at 37.5VDC
4 x LumiBar 56 cm strips in parallel: 1400mA(= 350mA x 4) at 37.5VDC
3. Combined circuit with LumiBar Nichia Optioslis LED strips
Series and parallel circuits can be combined, for example:
We create one group of two LumiBar Nichia Optioslis LED strips in series. Because one LED strip has 350mA at 39.5VDC, the group will have 350mA at 79VDC (= 39.5VDC x 2)
This group we connect in parallel to a second group, identical to the first (350mA at 79VDC). Then values of the string will be: 700mA (=350mA x 2) and 79VDC (=39.5V x 2).
The above can apply for single LEDs also. On our LumiFlex3098+ Pro Toshiba-SSC LED Strip Sunlike CRI98, segments of 7 LEDs in series are daisy-chained in parallel for a total length of 5 meters. The total circuit requires a constant voltage driver of 24VDC.
4. Selecting the LED driver for a string of LED strips
Before selecting the LED driver the current and voltage value of the string of LED strips must be known and the type of input: constant current or constant voltage.
Examples:
1 x LumiBar 56 cm Sunlike CRI98+ LED strip: 350mA at 39.5VDC will require the constant current LED driver Mean Well LPC-20-350 with 350mA output at 9 > 48VDC.
1 x PowerBar V3 LED Module Aluminium UV 365nm 12180mW 700mA at 44.4VDC can use a constant current LED driver Mean Well LCM-40 with 700mA output setting at 2 > 57VDC.
2 x LumiBar 56 cm Nichia Rsp0a Horticulture LED strips in parallel: 700mA(= 350mA x 2) at 37.5VDC can be connected to a constant current LED driver Mean Well LCM-40 with 700mA output setting at 2 > 57VDC.
3 x LumiBar 56 cm Sunlike CRI98+ LED strips in parallel: 1050mA(= 350mA x 3) at 39.5VDC require a constant current LED driver Mean Well LCM-60 with 1050mA output setting at 2 > 57VDC.
4 x LumiBar Nichia Optioslis LED strips in parallel: 1400mA(= 350mA x 4) at 39.5VDC need a constant current LED driver Mean Well LCM-60 with 1400mA output setting at 2 > 42VDC.
5 meters of LumiFlex3098+ Pro Toshiba-SSC LED Strip Sunlike CRI97 function at 24VDC and have a total power consumption of 96W (=19.2W x 5). In this case we can use one constant voltage LED driver at 24V, such as HLG-150H-24B with 150W maximum output.
10 meters of LumiFlex Samsung LED Strip CRI90 function at 24VDC and have a total power consumption of 126W (=12.6W x 5) can also work with the HLG-150H-24B.
Disclaimer:
This article is for informative purposes only. It is not a installation guide. LED strips our other electrical components should be installed by qualified personnel (such as an electrician).

 Lumistrips UK
Lumistrips UK Lumistrips US
Lumistrips US Lumistrips ES
Lumistrips ES Lumistrips PT
Lumistrips PT Lumistrips ITA
Lumistrips ITA











